Understanding Grey Market Stocks: The Hidden IPO Intelligence
Many investors eagerly anticipate the listing day of an Initial Public Offering (IPO) to decide whether to invest. However, experienced investors often position themselves weeks earlier using the grey market. This unofficial network allows trading before IPOs officially list on exchanges like the BSE and NSE, offering valuable insights into potential market sentiment. This section explores the complexities of grey market stocks, explaining how this unregulated market works and its importance for serious investors in India.
Decoding the Grey Market Mechanism
The grey market isn't a physical exchange, but a network of dealers and participants who trade IPO applications and shares before their official listing. This occurs outside the oversight of regulatory bodies. Pricing is driven by supply and demand, reflecting investor sentiment and speculation. The Indian grey market operates in this unregulated manner, facilitating trades before official listings.
For example, during an IPO on the NSE SME exchange, the grey market premium can fluctuate significantly. This makes the grey market a potentially more accurate indicator of market sentiment than traditional pre-IPO analysis. Learn more about Live IPO GMP: Live IPO GMP.
Key Players in the Grey Market
Several key players participate in the grey market ecosystem. Dealers act as intermediaries, facilitating buying and selling. Institutional participants, including high-net-worth individuals and proprietary trading desks, use the grey market to assess demand and refine their IPO strategies.
Retail investors are also increasingly active, seeking early opportunities for potential gains. The combined actions of these participants determine the grey market premium (GMP).
The Significance of Grey Market Premium (GMP)
The Grey Market Premium (GMP) represents the difference between the estimated listing price and the official IPO price. This key metric offers a glimpse into investor confidence. A positive GMP suggests the market anticipates a higher listing price than the IPO price, while a negative GMP indicates the opposite.
It's important to remember that GMP is only one factor to consider. Experienced investors use grey market data in conjunction with fundamental analysis to make informed decisions. For more information on pre-IPO, see: What is Pre-IPO.
Evolution of the Grey Market in India
The grey market in India has evolved considerably alongside the country's economic growth. With the rise in IPOs and increased retail investor participation, the market has become more complex. Understanding grey market dynamics is crucial for investors looking to capitalize on early investment opportunities.
While unregulated, the grey market contributes significantly to price discovery and provides a valuable preview of market sentiment, often proving remarkably accurate in predicting listing day performance.
Cracking The GMP Code: Your Crystal Ball For IPO Success

Grey Market Premium (GMP) is more than just a number; it offers valuable insights into market sentiment, providing potentially actionable intelligence for investors. However, understanding the nuances of different premium levels requires a deeper dive. It's not enough to simply acknowledge the GMP; we need to understand the factors driving its fluctuations.
Deciphering Premium Fluctuations
Interpreting GMP fluctuations involves distinguishing between genuine investor confidence and speculative activity. A consistently high GMP sustained over a longer period may suggest strong investor belief in the company's future prospects. On the other hand, a sudden, sharp spike could simply be short-term market hype, detached from the company's true value. This distinction is crucial for informed investment decisions.
Consider two IPOs with similar GMPs. One exhibits a steady, gradual increase, while the other experiences a dramatic surge right before listing. The steady growth might indicate sustainable investor interest, whereas the rapid jump could signal a speculative bubble.
Furthermore, high premiums can sometimes indicate overvaluation. Just because the market is willing to pay a premium doesn't necessarily mean the company's performance will justify it. Conversely, low premiums can occasionally reveal hidden value. A company with solid fundamentals but a low GMP might be undervalued by the market, presenting a potential opportunity for astute investors. The grey market in India plays a significant role in gauging investor sentiment before official listing. Research indicates these unofficial market prices often incorporate sentiment, influencing IPO underpricing in the Indian market. Learn more about this research: Sentiment Factor in Indian IPOs.
Timing: The Critical Factor
Timing plays a vital role in using GMP data effectively. Entering the grey market too early can expose investors to prolonged uncertainty and price volatility. Entering too late might mean missing out on potential gains. Seasoned investors often look for patterns in GMP movements to pinpoint optimal entry and exit points.
They analyze how GMP trends correlate with news releases, prevailing market conditions, and broader investor sentiment. This type of information is often available in research reports and market analyses focused on unlisted shares, particularly in the Indian market.
Frameworks for Utilizing GMP Data
Using GMP data effectively involves integrating it into a comprehensive investment strategy. Don't rely solely on GMP; combine it with thorough fundamental analysis. Carefully evaluate the company's financials, business model, and growth prospects to determine if the GMP aligns with the underlying value. You might find this resource helpful: Unlisted Share Price.
Real-World Case Studies
Numerous case studies illustrate how experienced investors have utilized GMP intelligence. By examining historical GMP data alongside post-listing company performance, they refine their understanding of how market sentiment translates into actual returns. This requires diligent observation and analysis, but the potential rewards can be significant. Understanding market cycles and the interplay of supply and demand are essential components of their approach.
This combined approach enables a more informed assessment of whether a specific GMP represents a genuine opportunity or inflated expectations. By integrating market intelligence with fundamental analysis, investors can better navigate the complexities of the grey market and position themselves for potential success in the dynamic world of IPOs.
Riding The IPO Wave: Recent Success Stories And Patterns
undefined
The recent increase in initial public offerings (IPOs) in India has created exciting investment opportunities. However, it's more important than ever to make informed decisions. By examining recent IPO successes, we can uncover key patterns that separate the winners from the rest. This knowledge empowers investors to potentially identify promising IPOs before they gain widespread recognition. You might be interested in: Our IPO page.
Case Studies: Unveiling Success Factors
Let's explore some specific examples. Companies like India Shelter Finance Corporation have effectively captured investor attention, demonstrating the importance of a compelling story and solid fundamentals. The grey market premium (GMP) is one indicator of this positive sentiment. Other companies like Doms Industries and Inox India underscore how important sector momentum and a clear growth trajectory are for attracting investors.
Analyzing these cases reveals a connection between subscription rates and grey market performance. High subscription rates often correlate with a positive GMP, suggesting strong investor confidence. Therefore, tracking both subscription levels and GMP can provide a valuable overview of market sentiment.
Decoding Market Sentiment Through Premium Trends
Rising premium trends in the grey market offer important clues about overall market sentiment. A steady rise in GMP often points to increasing confidence in a specific IPO. However, sudden, sharp increases may indicate speculative bubbles, calling for a more cautious approach. Understanding the difference between these scenarios requires careful analysis and an understanding of the company’s fundamentals. The grey market premium in India has been especially noteworthy recently, particularly during the 2023 IPO boom. In 2023, India witnessed 54 companies raise Rs 49,000 crore through IPOs, bringing increased focus to these rising premiums. For example, the India Shelter Finance Corporation IPO was subscribed over 2.34 times, demonstrating considerable investor interest. Find more detailed statistics here: Grey Market Trends and Insights in IPO.
Fundamentals vs. Speculation
The relationship between company fundamentals and grey market reception is vital. Sometimes, strong financials and growth potential justify high premiums. However, in other cases, they may be driven by speculation. Distinguishing between these situations is a cornerstone of successful grey market investing.
Consider this analogy: a well-maintained house in a desirable neighborhood might command a premium price, and that premium is likely justified. But a similar premium on a dilapidated house in the same area is probably due to speculation, driven by hype rather than actual value. Likewise, a high GMP for a company with weak fundamentals could be a sign of a speculative bubble.
Learning From Market Cycles
Investors can gain valuable knowledge by examining previous market cycles, including both wins and losses. Analyzing historical GMP data and comparing it to post-listing performance can help identify patterns and improve investment strategies. This allows investors to better position themselves for future IPOs. Read also: How to Participate in IPO. This involves looking beyond the hype and carefully considering the underlying factors influencing market sentiment.
Navigating Unregulated Waters: Smart Risk Management
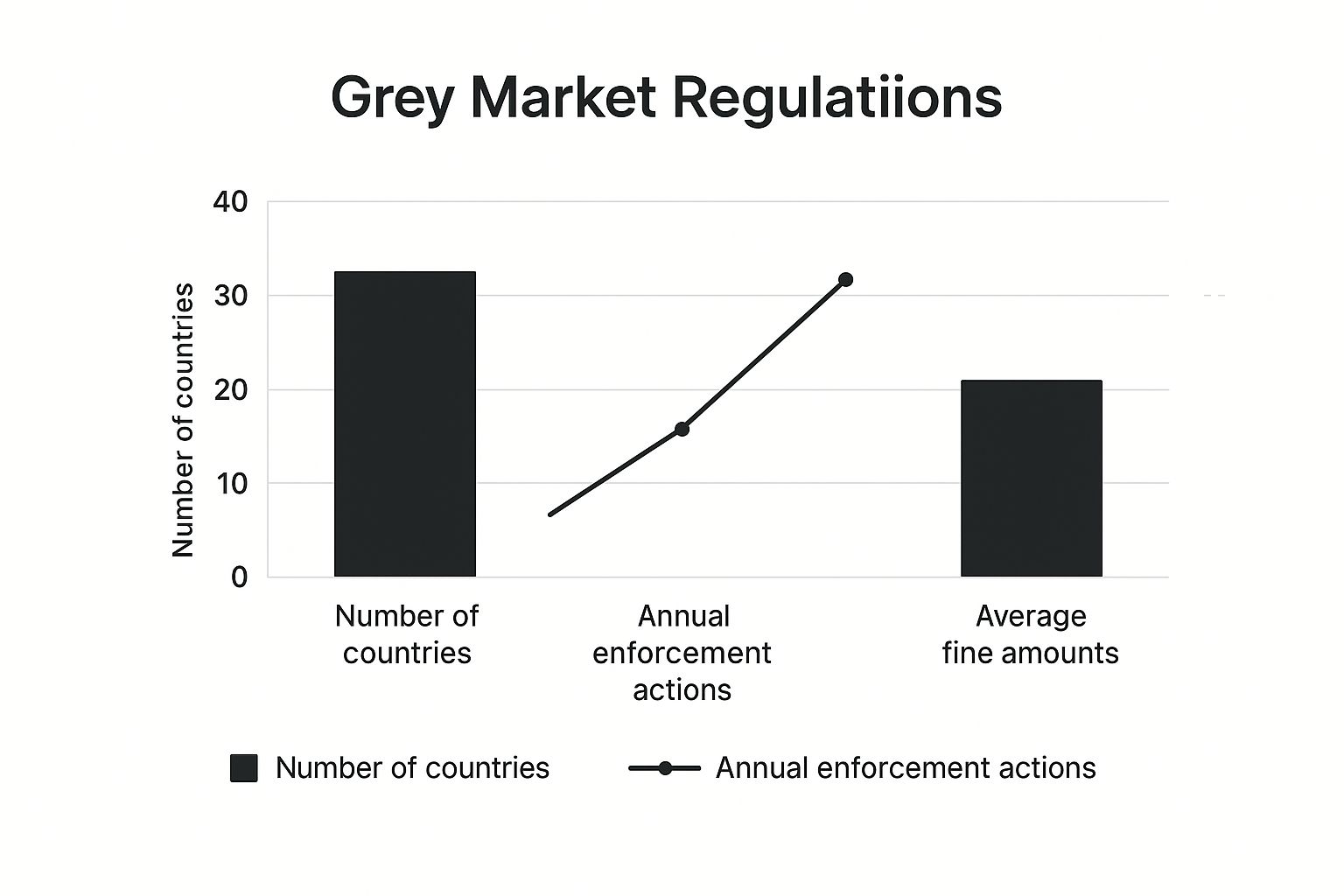
The infographic above visualizes data on the regulatory landscape of grey markets. It highlights the number of countries with formal regulations, enforcement actions, and average fines. The data suggests limited global oversight, underscoring the inherent risks of grey market trading. A cautious approach and diligent risk management are essential for investors in this space.
Understanding The Risks
The potential for early gains, particularly with IPOs, makes grey market stocks attractive. However, significant risks accompany this potential. These markets operate outside the purview of regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), increasing susceptibility to manipulation and fraud. This lack of regulation demands extra vigilance from investors.
Due Diligence and Verification
Due diligence is paramount before investing in grey market stocks. Verify the opportunity's legitimacy. Scrutinize the company's background, financials, and the credentials of involved intermediaries. This is particularly important in India, where informal networks largely drive the grey market.
Researching the historical performance of similar unlisted shares can offer valuable insights. Verifying the reputation and track record of the dealers involved can mitigate counterparty risks.
Managing Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk, the risk of default by the other party in a transaction, is amplified in grey markets. Mitigate this by working with established and reputable brokers or intermediaries. Building trust and verifying their credibility within the grey market network is crucial.
Think of it like lending money: the risk depends on the borrower's trustworthiness. Similarly, the counterparty's reliability dictates your potential loss exposure in grey market transactions.
To better understand the risks involved in grey market trading, let's compare them with traditional stock trading. The following table outlines key risk factors and their impact on both markets, along with potential mitigation strategies.
| Risk Factor | Grey Market Impact | Traditional Market Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
| Counterparty Risk | High - Risk of intermediary default | Lower - Regulated brokers and exchanges | Work with reputable intermediaries, verify credentials |
| Liquidity Risk | High - Difficulty buying/selling | Lower - Established exchanges and trading volumes | Diversification, smaller position sizes |
| Regulatory Risk | High - Lack of investor protection | Lower - Regulatory oversight and investor protection | Thorough due diligence, legal counsel |
| Fraud/Manipulation | High - Susceptible to scams | Lower - Regulatory monitoring and enforcement | Independent research, network verification |
| Price Volatility | High - Unregulated price fluctuations | Moderate - Market forces and regulations | Position sizing, stop-loss orders (in traditional markets) |





